// ObjectHashAggregateExec selected due to:
// 1. spark.sql.execution.useObjectHashAggregateExec internal flag is enabled
scala> val objectHashEnabled = spark.conf.get("spark.sql.execution.useObjectHashAggregateExec")
objectHashEnabled: String = true
// 2. The following data types are used in aggregateBufferAttributes
// BinaryType
// StringType
// ArrayType
// MapType
// ObjectType
// StructType
val dataset = Seq(
(0, Seq.empty[Int]),
(1, Seq(1, 1)),
(2, Seq(2, 2))).toDF("id", "nums")
import org.apache.spark.sql.functions.size
val q = dataset.
groupBy(size($"nums") as "group"). // <-- size over array
agg(collect_list("id") as "ids")
scala> q.explain
== Physical Plan ==
ObjectHashAggregate(keys=[size(nums#113)#127], functions=[collect_list(id#112, 0, 0)])
+- Exchange hashpartitioning(size(nums#113)#127, 200)
+- ObjectHashAggregate(keys=[size(nums#113) AS size(nums#113)#127], functions=[partial_collect_list(id#112, 0, 0)])
+- LocalTableScan [id#112, nums#113]
scala> println(q.queryExecution.sparkPlan.numberedTreeString)
00 ObjectHashAggregate(keys=[size(nums#113)#130], functions=[collect_list(id#112, 0, 0)], output=[group#117, ids#122])
01 +- ObjectHashAggregate(keys=[size(nums#113) AS size(nums#113)#130], functions=[partial_collect_list(id#112, 0, 0)], output=[size(nums#113)#130, buf#132])
02 +- LocalTableScan [id#112, nums#113]
// Going low level...watch your steps :)
// copied from HashAggregateExec as it is the preferred aggreate physical operator
// and HashAggregateExec is checked first
// When the check fails, ObjectHashAggregateExec is then checked
import q.queryExecution.optimizedPlan
import org.apache.spark.sql.catalyst.plans.logical.Aggregate
val aggLog = optimizedPlan.asInstanceOf[Aggregate]
import org.apache.spark.sql.catalyst.planning.PhysicalAggregation
import org.apache.spark.sql.catalyst.expressions.aggregate.AggregateExpression
val aggregateExpressions: Seq[AggregateExpression] = PhysicalAggregation.unapply(aggLog).get._2
val aggregateBufferAttributes = aggregateExpressions.
flatMap(_.aggregateFunction.aggBufferAttributes)
import org.apache.spark.sql.execution.aggregate.HashAggregateExec
// that's one of the reasons why ObjectHashAggregateExec was selected
// HashAggregateExec did not meet the requirements
scala> val useHash = HashAggregateExec.supportsAggregate(aggregateBufferAttributes)
useHash: Boolean = true
// collect_list aggregate function uses CollectList TypedImperativeAggregate under the covers
import org.apache.spark.sql.execution.aggregate.ObjectHashAggregateExec
scala> val useObjectHash = ObjectHashAggregateExec.supportsAggregate(aggregateExpressions)
useObjectHash: Boolean = true
val aggExec = q.queryExecution.sparkPlan.children.head.asInstanceOf[ObjectHashAggregateExec]
scala> println(aggExec.aggregateExpressions.head.numberedTreeString)
00 partial_collect_list(id#112, 0, 0)
01 +- collect_list(id#112, 0, 0)
02 +- id#112: intObjectHashAggregateExec Aggregate Physical Operator
ObjectHashAggregateExec is a unary physical operator that is created (indirectly through AggUtils.createAggregate) when:
-
…
|
Caution
|
FIXME |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
|
number of output rows |
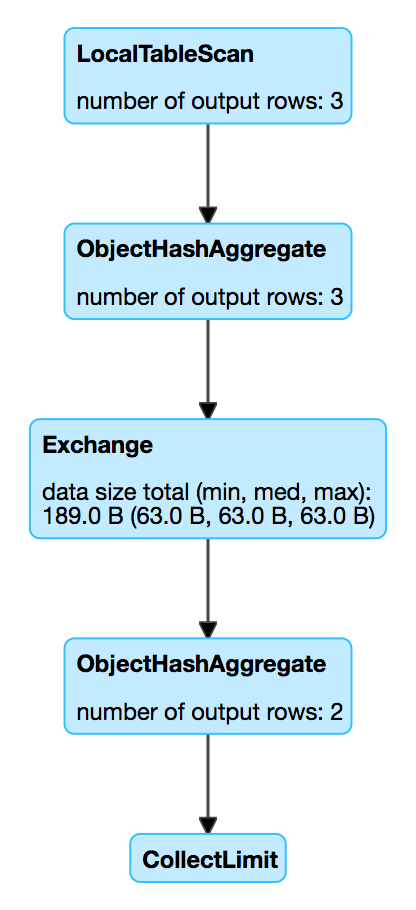
Figure 1. ObjectHashAggregateExec in web UI (Details for Query)
doExecute Method
|
Caution
|
FIXME |
supportsAggregate Method
supportsAggregate(aggregateExpressions: Seq[AggregateExpression]): BooleansupportsAggregate is enabled (i.e. returns true) if there is at least one TypedImperativeAggregate aggregate function in the input aggregateExpressions aggregate expressions.
|
Note
|
supportsAggregate is used exclusively when AggUtils.createAggregate selects an aggregate physical operator given aggregate expressions.
|
Creating ObjectHashAggregateExec Instance
ObjectHashAggregateExec takes the following when created:
-
Required child distribution expressions
-
Grouping named expressions
-
Aggregate attributes
-
Output named expressions
-
Child physical operator