GettingResultEvent(taskInfo: TaskInfo) extends DAGSchedulerEventDAGSchedulerEventProcessLoop — DAGScheduler Event Bus
DAGSchedulerEventProcessLoop (dag-scheduler-event-loop) is an EventLoop single "business logic" thread for processing DAGSchedulerEvent events.
|
Note
|
The purpose of the DAGSchedulerEventProcessLoop is to have a separate thread to process events asynchronously and serially, i.e. one by one, and let DAGScheduler do its work on the main thread.
|
| DAGSchedulerEvent | Event Handler | Trigger |
|---|---|---|
|
||
TaskSetManager informs |
||
Posted to inform
1. Completed Task instance (as 2. 3. Result of the task (as 4. Accumulator updates 5. TaskInfo |
||
|
||
Posted to notify
1. 2. NOTE: The input NOTE: handleExecutorLost is also called when |
||
TaskSetManager informs |
||
|
||
|
||
Posted when
1. A job identifier (as 2. A RDD (as 3. The function to execute (as 4. The partitions to compute (as 5. A 6. The JobListener to inform about the status of the stage. 7. |
||
Posted to inform
1. A job identifier (as 2. The ShuffleDependency 3. A 4. The JobListener to inform about the status of the stage. 5. |
||
|
||
|
||
|
When created, DAGSchedulerEventProcessLoop gets the reference to the owning DAGScheduler that it uses to call event handler methods on.
|
Note
|
DAGSchedulerEventProcessLoop uses java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque blocking deque that grows indefinitely, i.e. up to Integer.MAX_VALUE events.
|
AllJobsCancelled Event and…
|
Caution
|
FIXME |
GettingResultEvent Event and handleGetTaskResult Handler
GettingResultEvent is a DAGSchedulerEvent that triggers handleGetTaskResult (on a separate thread).
|
Note
|
GettingResultEvent is posted to inform DAGScheduler (through taskGettingResult) that a task fetches results.
|
handleGetTaskResult Handler
handleGetTaskResult(taskInfo: TaskInfo): UnithandleGetTaskResult merely posts SparkListenerTaskGettingResult (to LiveListenerBus Event Bus).
BeginEvent Event and handleBeginEvent Handler
BeginEvent(task: Task[_], taskInfo: TaskInfo) extends DAGSchedulerEventBeginEvent is a DAGSchedulerEvent that triggers handleBeginEvent (on a separate thread).
|
Note
|
BeginEvent is posted to inform DAGScheduler (through taskStarted) that a TaskSetManager starts a task.
|
handleBeginEvent Handler
handleBeginEvent(task: Task[_], taskInfo: TaskInfo): UnithandleBeginEvent looks the stage of task up in stageIdToStage internal registry to compute the last attempt id (or -1 if not available) and posts SparkListenerTaskStart (to listenerBus event bus).
JobGroupCancelled Event and handleJobGroupCancelled Handler
JobGroupCancelled(groupId: String) extends DAGSchedulerEventJobGroupCancelled is a DAGSchedulerEvent that triggers handleJobGroupCancelled (on a separate thread).
|
Note
|
JobGroupCancelled is posted when DAGScheduler is informed (through cancelJobGroup) that SparkContext was requested to cancel a job group.
|
handleJobGroupCancelled Handler
handleJobGroupCancelled(groupId: String): UnithandleJobGroupCancelled finds active jobs in a group and cancels them.
Internally, handleJobGroupCancelled computes all the active jobs (registered in the internal collection of active jobs) that have spark.jobGroup.id scheduling property set to groupId.
handleJobGroupCancelled then cancels every active job in the group one by one and the cancellation reason: "part of cancelled job group [groupId]".
Getting Notified that ShuffleDependency Was Submitted — handleMapStageSubmitted Handler
handleMapStageSubmitted(
jobId: Int,
dependency: ShuffleDependency[_, _, _],
callSite: CallSite,
listener: JobListener,
properties: Properties): Unit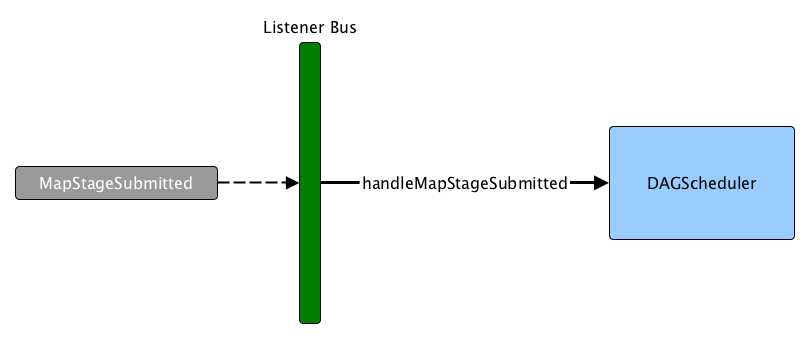
MapStageSubmitted Event HandlinghandleMapStageSubmitted finds or creates a new ShuffleMapStage for the input ShuffleDependency and jobId.
handleMapStageSubmitted creates an ActiveJob (with the input jobId, callSite, listener and properties, and the ShuffleMapStage).
handleMapStageSubmitted clears the internal cache of RDD partition locations.
|
Caution
|
FIXME Why is this clearing here so important? |
You should see the following INFO messages in the logs:
INFO DAGScheduler: Got map stage job [id] ([callSite]) with [number] output partitions
INFO DAGScheduler: Final stage: [stage] ([name])
INFO DAGScheduler: Parents of final stage: [parents]
INFO DAGScheduler: Missing parents: [missingStages]handleMapStageSubmitted registers the new job in jobIdToActiveJob and activeJobs internal registries, and with the final ShuffleMapStage.
|
Note
|
ShuffleMapStage can have multiple ActiveJobs registered.
|
handleMapStageSubmitted finds all the registered stages for the input jobId and collects their latest StageInfo.
Ultimately, handleMapStageSubmitted posts SparkListenerJobStart message to LiveListenerBus and submits the ShuffleMapStage.
In case the ShuffleMapStage could be available already, handleMapStageSubmitted marks the job finished.
|
Note
|
DAGScheduler requests MapOutputTrackerMaster for statistics for ShuffleDependency that it uses for handleMapStageSubmitted.
|
|
Note
|
MapOutputTrackerMaster is passed in when DAGScheduler is created.
|
When handleMapStageSubmitted could not find or create a ShuffleMapStage, you should see the following WARN message in the logs.
WARN Creating new stage failed due to exception - job: [id]handleMapStageSubmitted notifies listener about the job failure and exits.
|
Note
|
MapStageSubmitted event processing is very similar to JobSubmitted events.
|
|
Tip
|
The difference between handleMapStageSubmitted and handleJobSubmitted:
|
TaskSetFailed Event and handleTaskSetFailed Handler
TaskSetFailed(
taskSet: TaskSet,
reason: String,
exception: Option[Throwable])
extends DAGSchedulerEventTaskSetFailed is a DAGSchedulerEvent that triggers handleTaskSetFailed method.
|
Note
|
TaskSetFailed is posted when DAGScheduler is requested to cancel a TaskSet.
|
handleTaskSetFailed Handler
handleTaskSetFailed(
taskSet: TaskSet,
reason: String,
exception: Option[Throwable]): UnithandleTaskSetFailed looks the stage (of the input taskSet) up in the internal stageIdToStage registry and aborts it.
ResubmitFailedStages Event and resubmitFailedStages Handler
ResubmitFailedStages extends DAGSchedulerEventResubmitFailedStages is a DAGSchedulerEvent that triggers resubmitFailedStages method.
|
Note
|
ResubmitFailedStages is posted for FetchFailed case in handleTaskCompletion.
|
resubmitFailedStages Handler
resubmitFailedStages(): UnitresubmitFailedStages iterates over the internal collection of failed stages and submits them.
|
Note
|
resubmitFailedStages does nothing when there are no failed stages reported.
|
You should see the following INFO message in the logs:
INFO Resubmitting failed stagesresubmitFailedStages clears the internal cache of RDD partition locations first. It then makes a copy of the collection of failed stages so DAGScheduler can track failed stages afresh.
|
Note
|
At this point DAGScheduler has no failed stages reported.
|
The previously-reported failed stages are sorted by the corresponding job ids in incremental order and resubmitted.
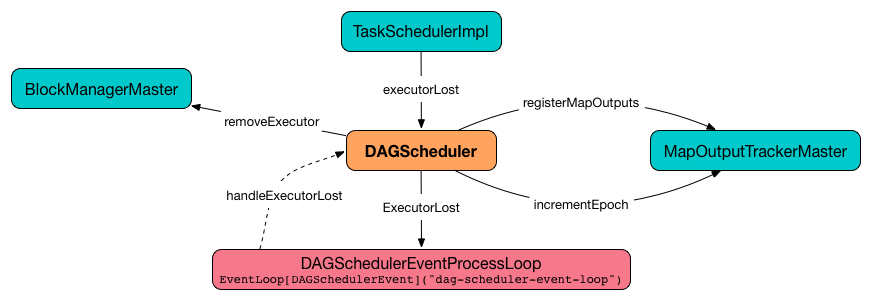
Getting Notified that Executor Is Lost — handleExecutorLost Handler
handleExecutorLost(
execId: String,
filesLost: Boolean,
maybeEpoch: Option[Long] = None): UnithandleExecutorLost checks whether the input optional maybeEpoch is defined and if not requests the current epoch from MapOutputTrackerMaster.
|
Note
|
MapOutputTrackerMaster is passed in (as mapOutputTracker) when DAGScheduler is created.
|
|
Caution
|
FIXME When is maybeEpoch passed in?
|
Recurring ExecutorLost events lead to the following repeating DEBUG message in the logs:
DEBUG Additional executor lost message for [execId] (epoch [currentEpoch])|
Note
|
handleExecutorLost handler uses DAGScheduler's failedEpoch and FIXME internal registries.
|
Otherwise, when the executor execId is not in the list of executor lost or the executor failure’s epoch is smaller than the input maybeEpoch, the executor’s lost event is recorded in failedEpoch internal registry.
|
Caution
|
FIXME Describe the case above in simpler non-technical words. Perhaps change the order, too. |
You should see the following INFO message in the logs:
INFO Executor lost: [execId] (epoch [epoch])|
Caution
|
FIXME Review what’s filesLost.
|
handleExecutorLost exits unless the ExecutorLost event was for a map output fetch operation (and the input filesLost is true) or external shuffle service is not used.
In such a case, you should see the following INFO message in the logs:
INFO Shuffle files lost for executor: [execId] (epoch [epoch])handleExecutorLost walks over all ShuffleMapStages in DAGScheduler’s shuffleToMapStage internal registry and do the following (in order):
-
ShuffleMapStage.removeOutputsOnExecutor(execId)is called
In case DAGScheduler’s shuffleToMapStage internal registry has no shuffles registered, MapOutputTrackerMaster is requested to increment epoch.
Ultimatelly, DAGScheduler clears the internal cache of RDD partition locations.
JobCancelled Event and handleJobCancellation Handler
JobCancelled(jobId: Int) extends DAGSchedulerEventJobCancelled is a DAGSchedulerEvent that triggers handleJobCancellation method (on a separate thread).
|
Note
|
JobCancelled is posted when DAGScheduler is requested to cancel a job.
|
handleJobCancellation Handler
handleJobCancellation(jobId: Int, reason: String = "")handleJobCancellation first makes sure that the input jobId has been registered earlier (using jobIdToStageIds internal registry).
If the input jobId is not known to DAGScheduler, you should see the following DEBUG message in the logs:
DEBUG DAGScheduler: Trying to cancel unregistered job [jobId]Otherwise, handleJobCancellation fails the active job and all independent stages (by looking up the active job using jobIdToActiveJob) with failure reason:
Job [jobId] cancelled [reason] Getting Notified That Task Has Finished — handleTaskCompletion Handler
handleTaskCompletion(event: CompletionEvent): Unit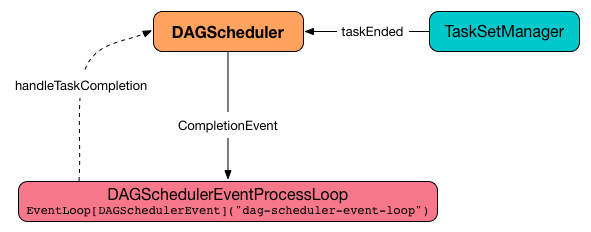
|
Note
|
CompletionEvent holds contextual information about the completed task.
|
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
|
Completed Task instance for a stage, partition and stage attempt. |
|
|
|
Result of the task |
|
Accumulators with…FIXME |
|
handleTaskCompletion starts by notifying OutputCommitCoordinator that a task completed.
handleTaskCompletion re-creates TaskMetrics (using accumUpdates accumulators of the input event).
|
Note
|
TaskMetrics can be empty when the task has failed. |
handleTaskCompletion announces task completion application-wide (by posting a SparkListenerTaskEnd to LiveListenerBus).
handleTaskCompletion checks the stage of the task out in the stageIdToStage internal registry and if not found, it simply exits.
handleTaskCompletion branches off per TaskEndReason (as event.reason).
| TaskEndReason | Description |
|---|---|
Acts according to the type of the task that completed, i.e. ShuffleMapTask and ResultTask. |
|
|
Updates accumulators (with partial values from the task). |
|
Does nothing |
|
Does nothing |
|
Does nothing |
|
Does nothing |
|
Does nothing |
Handling Successful Task Completion
When a task has finished successfully (i.e. Success end reason), handleTaskCompletion marks the partition as no longer pending (i.e. the partition the task worked on is removed from pendingPartitions of the stage).
|
Note
|
A Stage tracks its own pending partitions using pendingPartitions property.
|
handleTaskCompletion branches off given the type of the task that completed, i.e. ShuffleMapTask and ResultTask.
Handling Successful ResultTask Completion
For ResultTask, the stage is assumed a ResultStage.
handleTaskCompletion finds the ActiveJob associated with the ResultStage.
|
Note
|
ResultStage tracks the optional ActiveJob as activeJob property. There could only be one active job for a ResultStage.
|
If there is no job for the ResultStage, you should see the following INFO message in the logs:
INFO DAGScheduler: Ignoring result from [task] because its job has finishedOtherwise, when the ResultStage has a ActiveJob, handleTaskCompletion checks the status of the partition output for the partition the ResultTask ran for.
|
Note
|
ActiveJob tracks task completions in finished property with flags for every partition in a stage. When the flag for a partition is enabled (i.e. true), it is assumed that the partition has been computed (and no results from any ResultTask are expected and hence simply ignored).
|
|
Caution
|
FIXME Describe why could a partition has more ResultTask running.
|
handleTaskCompletion ignores the CompletionEvent when the partition has already been marked as completed for the stage and simply exits.
handleTaskCompletion updates accumulators.
The partition for the ActiveJob (of the ResultStage) is marked as computed and the number of partitions calculated increased.
|
Note
|
ActiveJob tracks what partitions have already been computed and their number.
|
If the ActiveJob has finished (when the number of partitions computed is exactly the number of partitions in a stage) handleTaskCompletion does the following (in order):
-
Announces the job completion application-wide (by posting a SparkListenerJobEnd to LiveListenerBus).
In the end, handleTaskCompletion notifies JobListener of the ActiveJob that the task succeeded.
|
Note
|
A task succeeded notification holds the output index and the result. |
When the notification throws an exception (because it runs user code), handleTaskCompletion notifies JobListener about the failure (wrapping it inside a SparkDriverExecutionException exception).
Handling Successful ShuffleMapTask Completion
For ShuffleMapTask, the stage is assumed a ShuffleMapStage.
handleTaskCompletion updates accumulators.
The task’s result is assumed MapStatus that knows the executor where the task has finished.
You should see the following DEBUG message in the logs:
DEBUG DAGScheduler: ShuffleMapTask finished on [execId]If the executor is registered in failedEpoch internal registry and the epoch of the completed task is not greater than that of the executor (as in failedEpoch registry), you should see the following INFO message in the logs:
INFO DAGScheduler: Ignoring possibly bogus [task] completion from executor [executorId]Otherwise, handleTaskCompletion registers the MapStatus result for the partition with the stage (of the completed task).
handleTaskCompletion does more processing only if the ShuffleMapStage is registered as still running (in runningStages internal registry) and the ShuffleMapStage stage has no pending partitions to compute.
The ShuffleMapStage is marked as finished.
You should see the following INFO messages in the logs:
INFO DAGScheduler: looking for newly runnable stages
INFO DAGScheduler: running: [runningStages]
INFO DAGScheduler: waiting: [waitingStages]
INFO DAGScheduler: failed: [failedStages]handleTaskCompletion registers the shuffle map outputs of the ShuffleDependency with MapOutputTrackerMaster (with the epoch incremented) and clears internal cache of the stage’s RDD block locations.
|
Note
|
MapOutputTrackerMaster is given when DAGScheduler is created.
|
If the ShuffleMapStage stage is ready, all active jobs of the stage (aka map-stage jobs) are marked as finished (with MapOutputStatistics from MapOutputTrackerMaster for the ShuffleDependency).
|
Note
|
A ShuffleMapStage stage is ready (aka available) when all partitions have shuffle outputs, i.e. when their tasks have completed.
|
Eventually, handleTaskCompletion submits waiting child stages (of the ready ShuffleMapStage).
If however the ShuffleMapStage is not ready, you should see the following INFO message in the logs:
INFO DAGScheduler: Resubmitting [shuffleStage] ([shuffleStage.name]) because some of its tasks had failed: [missingPartitions]In the end, handleTaskCompletion submits the ShuffleMapStage for execution.
TaskEndReason: Resubmitted
For Resubmitted case, you should see the following INFO message in the logs:
INFO Resubmitted [task], so marking it as still runningThe task (by task.partitionId) is added to the collection of pending partitions of the stage (using stage.pendingPartitions).
|
Tip
|
A stage knows how many partitions are yet to be calculated. A task knows about the partition id for which it was launched. |
Task Failed with FetchFailed Exception — TaskEndReason: FetchFailed
FetchFailed(
bmAddress: BlockManagerId,
shuffleId: Int,
mapId: Int,
reduceId: Int,
message: String)
extends TaskFailedReason| Name | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Used when… |
|
Used when… |
|
Used when… |
|
Used when… |
|
Note
|
A task knows about the id of the stage it belongs to. |
When FetchFailed happens, stageIdToStage is used to access the failed stage (using task.stageId and the task is available in event in handleTaskCompletion(event: CompletionEvent)). shuffleToMapStage is used to access the map stage (using shuffleId).
If failedStage.latestInfo.attemptId != task.stageAttemptId, you should see the following INFO in the logs:
INFO Ignoring fetch failure from [task] as it's from [failedStage] attempt [task.stageAttemptId] and there is a more recent attempt for that stage (attempt ID [failedStage.latestInfo.attemptId]) running|
Caution
|
FIXME What does failedStage.latestInfo.attemptId != task.stageAttemptId mean?
|
And the case finishes. Otherwise, the case continues.
If the failed stage is in runningStages, the following INFO message shows in the logs:
INFO Marking [failedStage] ([failedStage.name]) as failed due to a fetch failure from [mapStage] ([mapStage.name])markStageAsFinished(failedStage, Some(failureMessage)) is called.
|
Caution
|
FIXME What does markStageAsFinished do?
|
If the failed stage is not in runningStages, the following DEBUG message shows in the logs:
DEBUG Received fetch failure from [task], but its from [failedStage] which is no longer runningWhen disallowStageRetryForTest is set, abortStage(failedStage, "Fetch failure will not retry stage due to testing config", None) is called.
|
Caution
|
FIXME Describe disallowStageRetryForTest and abortStage.
|
If the number of fetch failed attempts for the stage exceeds the allowed number, the failed stage is aborted with the reason:
[failedStage] ([name]) has failed the maximum allowable number of times: 4. Most recent failure reason: [failureMessage]If there are no failed stages reported (DAGScheduler.failedStages is empty), the following INFO shows in the logs:
INFO Resubmitting [mapStage] ([mapStage.name]) and [failedStage] ([failedStage.name]) due to fetch failureAnd the following code is executed:
messageScheduler.schedule(
new Runnable {
override def run(): Unit = eventProcessLoop.post(ResubmitFailedStages)
}, DAGScheduler.RESUBMIT_TIMEOUT, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)|
Caution
|
FIXME What does the above code do? |
For all the cases, the failed stage and map stages are both added to the internal registry of failed stages.
If mapId (in the FetchFailed object for the case) is provided, the map stage output is cleaned up (as it is broken) using mapStage.removeOutputLoc(mapId, bmAddress) and MapOutputTrackerMaster.unregisterMapOutput(shuffleId, mapId, bmAddress) methods.
|
Caution
|
FIXME What does mapStage.removeOutputLoc do?
|
If BlockManagerId (as bmAddress in the FetchFailed object) is defined, handleTaskCompletion notifies DAGScheduler that an executor was lost (with filesLost enabled and maybeEpoch from the Task that completed).
StageCancelled Event and handleStageCancellation Handler
StageCancelled(stageId: Int) extends DAGSchedulerEventStageCancelled is a DAGSchedulerEvent that triggers handleStageCancellation (on a separate thread).
handleStageCancellation Handler
handleStageCancellation(stageId: Int): UnithandleStageCancellation checks if the input stageId was registered earlier (in the internal stageIdToStage registry) and if it was attempts to cancel the associated jobs (with "because Stage [stageId] was cancelled" cancellation reason).
|
Note
|
A stage tracks the jobs it belongs to using jobIds property.
|
If the stage stageId was not registered earlier, you should see the following INFO message in the logs:
INFO No active jobs to kill for Stage [stageId]|
Note
|
handleStageCancellation is the result of executing SparkContext.cancelStage(stageId: Int) that is called from the web UI (controlled by spark.ui.killEnabled).
|
handleJobSubmitted Handler
handleJobSubmitted(
jobId: Int,
finalRDD: RDD[_],
func: (TaskContext, Iterator[_]) => _,
partitions: Array[Int],
callSite: CallSite,
listener: JobListener,
properties: Properties)handleJobSubmitted creates a new ResultStage (as finalStage in the picture below) given the input finalRDD, func, partitions, jobId and callSite.
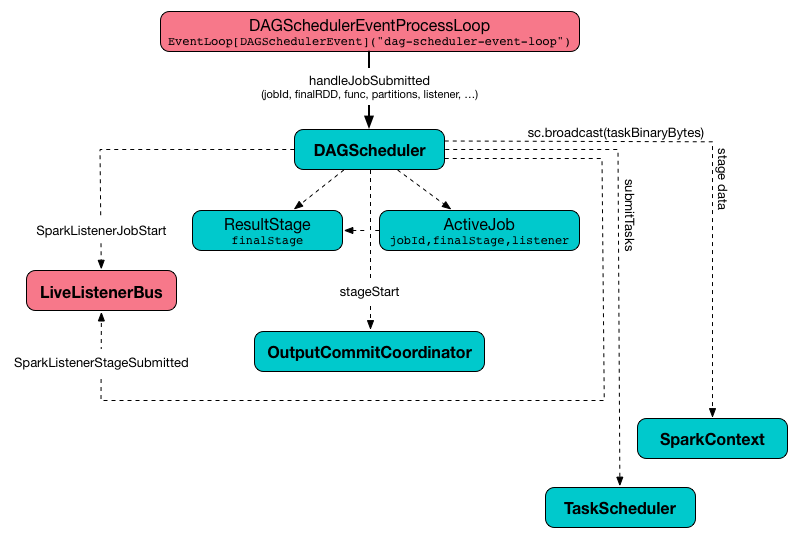
DAGScheduler.handleJobSubmitted MethodhandleJobSubmitted creates an ActiveJob (with the input jobId, callSite, listener, properties, and the ResultStage).
handleJobSubmitted clears the internal cache of RDD partition locations.
|
Caution
|
FIXME Why is this clearing here so important? |
You should see the following INFO messages in the logs:
INFO DAGScheduler: Got job [id] ([callSite]) with [number] output partitions
INFO DAGScheduler: Final stage: [stage] ([name])
INFO DAGScheduler: Parents of final stage: [parents]
INFO DAGScheduler: Missing parents: [missingStages]handleJobSubmitted then registers the new job in jobIdToActiveJob and activeJobs internal registries, and with the final ResultStage.
|
Note
|
ResultStage can only have one ActiveJob registered.
|
handleJobSubmitted finds all the registered stages for the input jobId and collects their latest StageInfo.
Ultimately, handleJobSubmitted posts SparkListenerJobStart message to LiveListenerBus and submits the stage.
ExecutorAdded Event and handleExecutorAdded Handler
ExecutorAdded(execId: String, host: String) extends DAGSchedulerEventExecutorAdded is a DAGSchedulerEvent that triggers handleExecutorAdded method (on a separate thread).
Removing Executor From failedEpoch Registry — handleExecutorAdded Handler
handleExecutorAdded(execId: String, host: String)handleExecutorAdded checks if the input execId executor was registered in failedEpoch and, if it was, removes it from the failedEpoch registry.
You should see the following INFO message in the logs:
INFO Host added was in lost list earlier: [host]